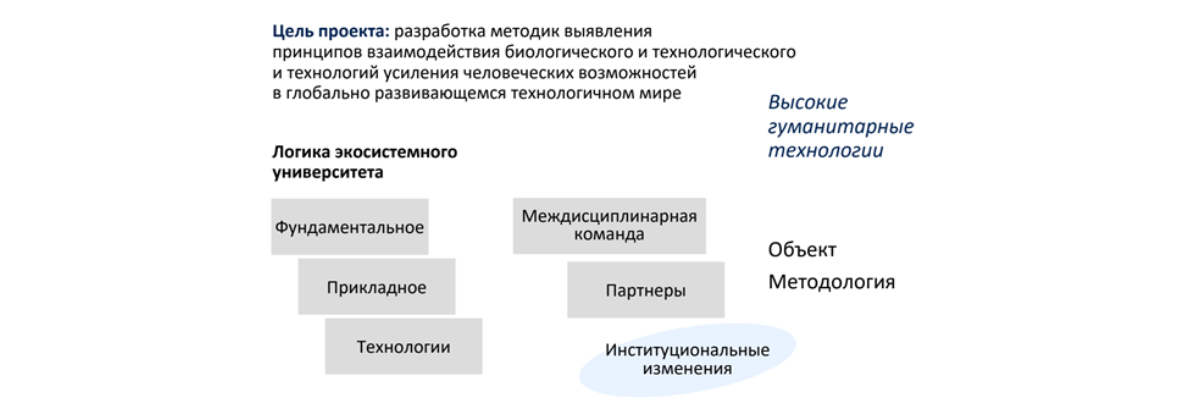
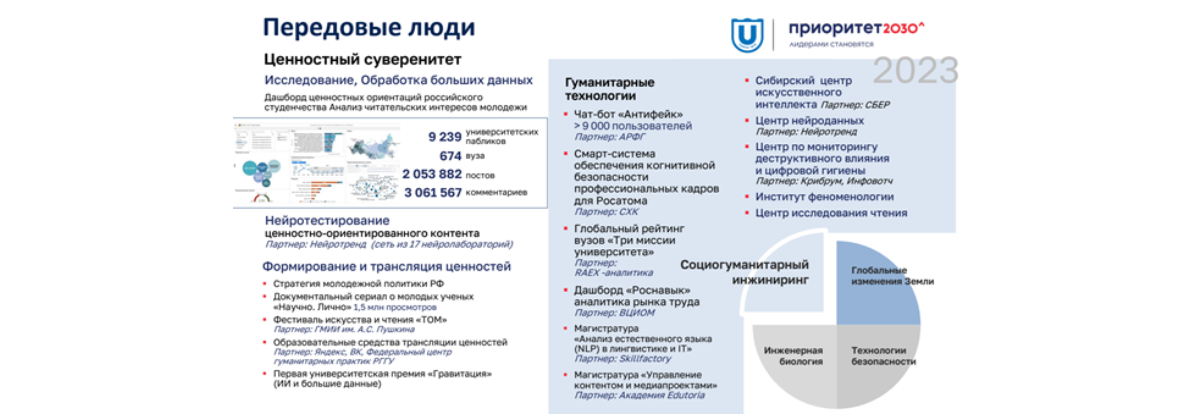
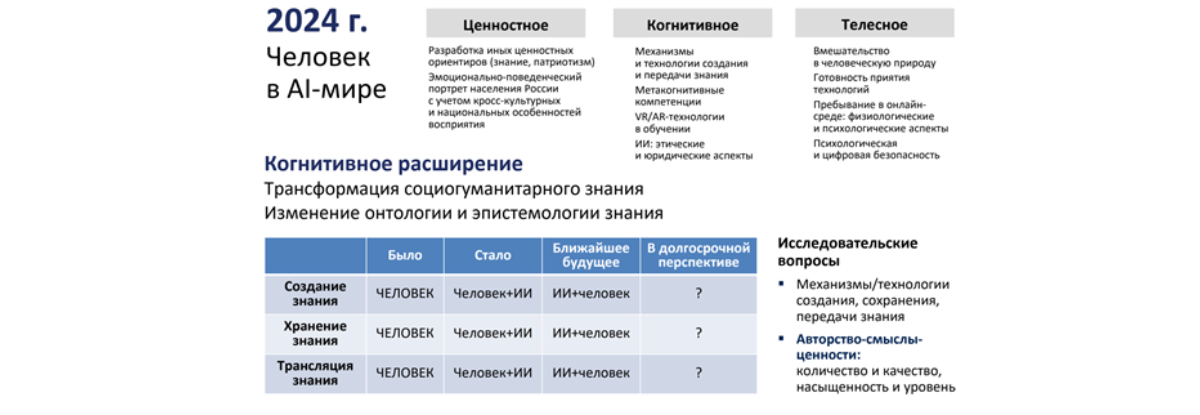
Lalas
Star
- Joined
- Nov 8, 2022
- Messages
- 1,383

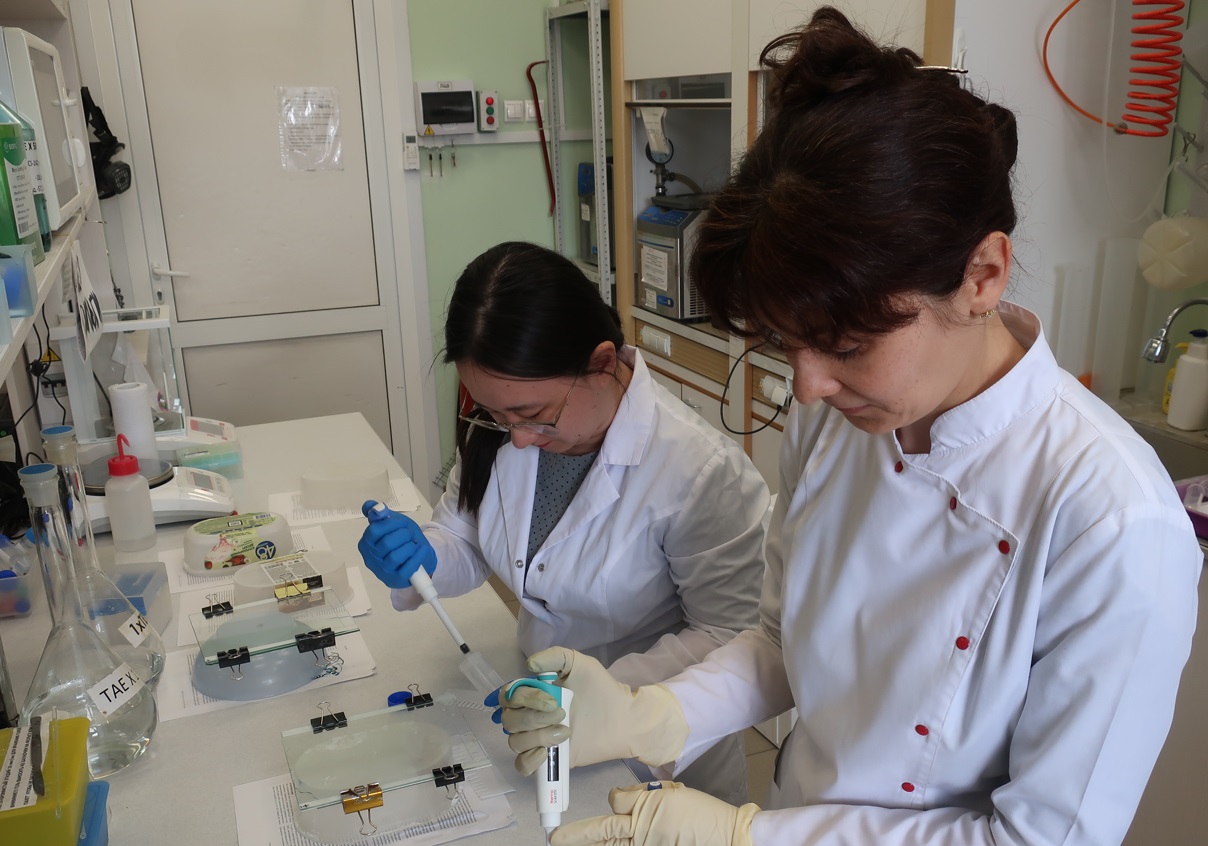
Создана сверхгибкая основа для биосовместимой флеш-памяти
Материал разработан на базе полимерных и оксидных пленок
The material is developed on the basis of polymer and oxide films

MOSCOW, March 14, 2024. Researchers from Russia have developed an ultra-flexible material based on polymer and oxide films, which is able to store information and at the same time endure a large number of bends and stretches. It can be used as a basis for smart sensors, neural implants and other devices, according to the MIPT Center for Science Communication.
"To show that the device has unprecedented mechanical properties – it can withstand repeated folding in half – we designed an entire setup. On it, we demonstrated that the flexible flash drive we created can withstand 150 thousand cycles of bending and stretching with a load of one and a half kilograms," said Anastasia Chuprik, head of the Laboratory of Advanced Data Storage Concepts at MIPT (Dolgoprudny), whose words are quoted by the Communication Center. She also stressed that scientists would not have been able to achieve such figures manually.
The basis for the development of flexible memory created by Chuprik and her colleagues is a film made of polyimide polymer material, inside which an ultra-thin layer of hafnium oxide is embedded, which also contains zirconium atoms. This material is the so-called ferroelectric (ferroelectric) - a substance in which the distribution of electrons can be controlled using electric fields.
This makes it possible to use films and crystals of such substances to create a new type of non-volatile memory, where data is stored in the form of "piles" of electrons. According to engineers and physicists, it will work as fast as modern RAM, but at the same time, information from it will not disappear when the power is turned off, which is akin to flash chips. In the case of hafnium oxide, these films can have a very low thickness, on the order of 10 nanometers.
"Hafnium oxide films exhibit ferroelectric properties when they are very thin: from 4 to 30 nanometers, and with other materials you need a thickness of more than 100 nanometers. Therefore, we expected that the material would be very flexible and would retain its ferroelectric properties under bending and various mechanical deformations," Chuprik explained.
For example, scientists have created a flexible prototype of flash memory based on a film made of polyimide and hafnium and zirconium oxides, which has a high level of biocompatibility. Subsequent tests of its operation showed that the device did not lose its ability to read and write information after 150,000 deformation cycles. This paves the way for the creation of ultra-flexible information storage systems, the researchers concluded."
8.01.2024
..
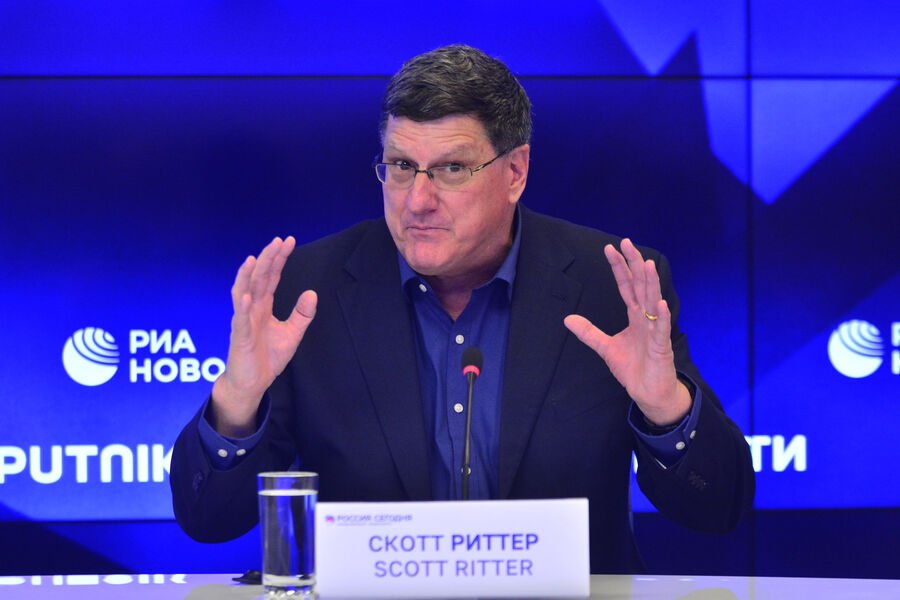
"What I see now is a new Russia! Many wanted Russia to collapse and no longer be able to rise from its knees. But the Russians took it all together, got together and did what they have now! It's an incredible example of pride!" said Scott Ritter.