Lalas
Star
- Joined
- Nov 8, 2022
- Messages
- 1,383

St. Petersburg State Electrotechnical University "LETI" named after V.I.Ulyanov (Lenin) SPbGETU "LETI"

Программа «Приоритет-2030»
СПбГЭТУ «ЛЭТИ» вошел в число 46 университетов-участников программы «Приоритет 2030», которые получат гранты по направлениям «Исследовательское лидерство» и «Территориальное и (или) отраслевое лидерство»

MISSION AND STRATEGIC GOAL OF SPbSETU "LETI"
within the framework of the PRIORITY 2030 program
The mission of the University is to ensure the scientific and technological leadership of industries in the areas of competence relevant to the University through advanced research and development, training of the engineering elite and harmonious personal development.
The strategic goal of the University is the formation of a reference R&D (research and development) A university in which advanced research and development, as well as training of engineering personnel, are aimed at technological development and digital transformation of enterprises in specialized sectors of the economy and territories on the basis of system integration and synergetic unification of the personnel, intellectual and corporate potentials of the University, academic and industrial partners.
To learn more…
The university relies on revolutionary changes in three directions: research, markets, education.
A revolution in research on the root markets for SPbGETU "LETI", the answer to which will be the formation of key competencies and the creation of R&D laboratories in promising areas of research.
The revolution in the markets is the University's response to which will be active participation in the formation of interdisciplinary frontiers at the junction of different sectors of industry, in expanding the areas of application of accumulated knowledge and advanced approaches (including technological foresight, design thinking, system engineering), in building promising technological maps of the development of industries and companies.
The revolution in education is the answer to which SPbSETU "LETI" sees in the formation of new ways of thinking, the creation of an academic environment and services, the promotion of knowledge around the world, international openness and cooperation, the creation of conditions for attracting and developing talents.
It is planned to create a space for experiments at SPbSETU LETI: to launch and scale the best practices in research, interaction with industry and organizations of the Russian Academy of Sciences, implementation of advanced educational programs, development of technological services to support startups, including in the formats of engineering centers; work in the format of business clubs with industrial partners, for discussion current trends in science (foresight, reports); formation and support of change teams.
..."
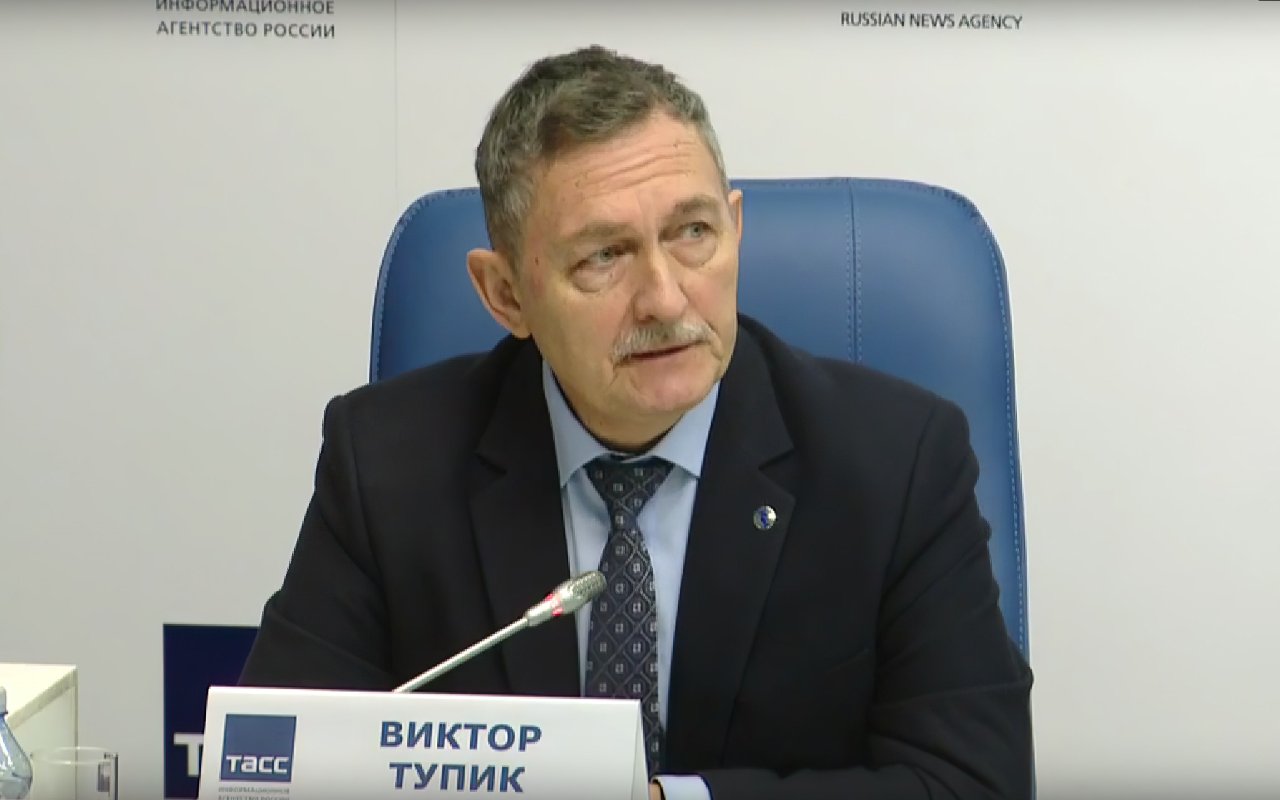

«Подготовка кадров и планы по внедрению разработок»: проректор ЛЭТИ Виктор Тупик о реализации программы «Приоритет 2030»
За прошедший год СПбГЭТУ «ЛЭТИ» получил ряд конкретных результатов по стратегическим проектам программы развития вуза, внедрение которых планируется начать уже в 2023 году совместно с индустриальными партнерами в сфере электроники.
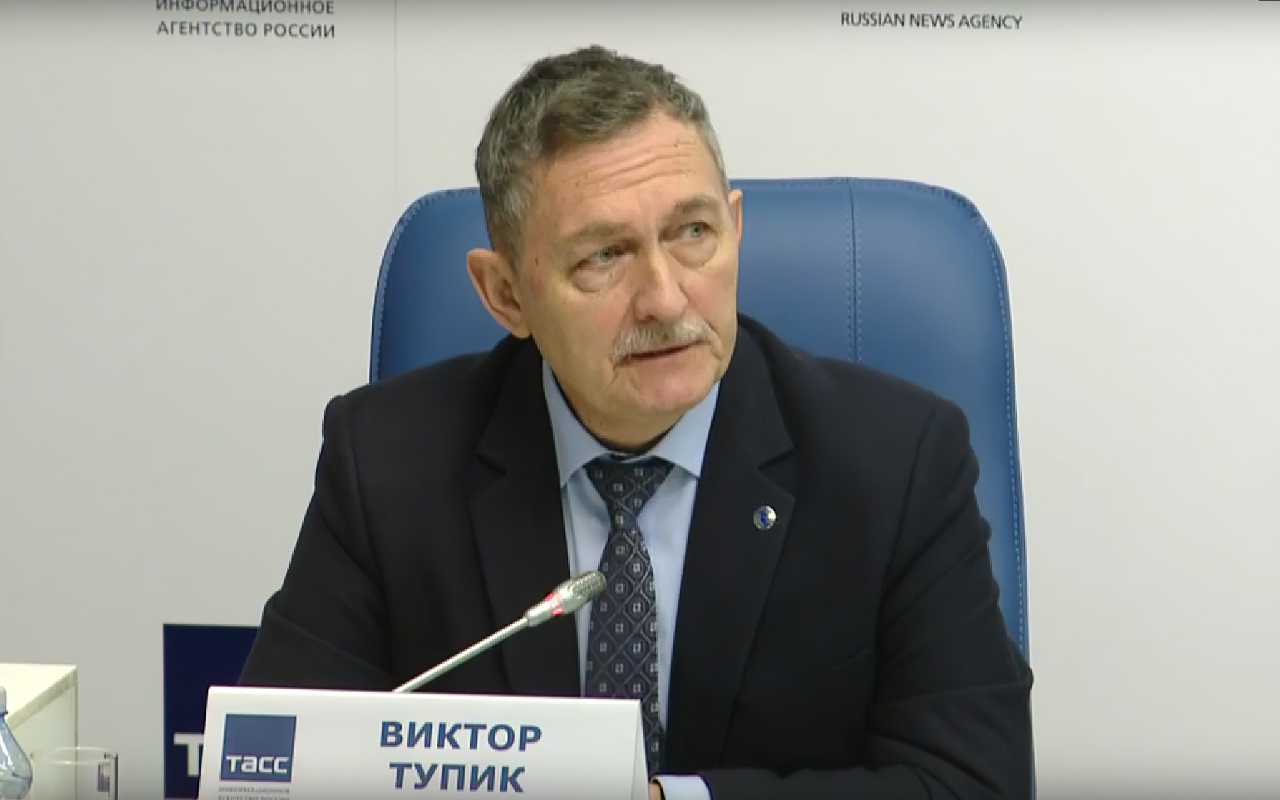

Over the past year, SPbSETU "LETI" has received a number of concrete results on strategic projects of the university development program, the implementation of which is planned to begin in 2023 together with industrial partners in the field of electronics.
26.01.2023
On January 25, a press conference dedicated to the results of the first year of participation of universities of the Northern capital in the federal program of strategic academic leadership "Priority 2030" was held at the TASS regional information center in St. Petersburg. The meeting was attended by Vice-Governor of St. Petersburg Vladimir Nikolaevich Knyaginin, Vice-Rector for Scientific Work of St. Petersburg State Technical University "LETI" Viktor Anatolyevich Tupik, as well as representatives of other universities of the city who participate in the program.
Speaking at a press conference, Viktor Anatolyevich stressed that the LETI development program is focused around two important aspects: training personnel for high-tech branches of domestic industry, as well as bridging the gap between the sphere of scientific research and the real sector of the economy.
The Vice-Rector noted that the basis for solving these tasks at LETI are three interrelated strategic projects: "Nanoheterostructural electronics, photonics and radiophotonics", which is the key, "New technologies of information connectivity of objects and territories", as well as "Technologies of strong hybrid intelligence for diagnosis, prevention, treatment and rehabilitation in applied medicine".
"The key strategic project concerns the development of new types of semiconductor nanoheterostructures. This direction will allow creating more efficient components and devices for mass implementation at enterprises. Our university has a strong foundation for conducting research in this area. Let me remind you that it was started by the Nobel laureate Zhores Ivanovich Alferov, who in the past was a student and graduate of LETI, and then a professor and head of the department of our university."
Vice-Rector for Scientific Work of SPBSET "LETI" Viktor Anatolyevich Tupik
He also clarified that over the past year, LETI scientists, during the implementation of this strategic project, have worked out methods for studying and creating nanoheterostructures, on the basis of which they have developed a line of photonic integrated circuits that are promising for creating a new class of electronic component base. Libraries of technological processes and components necessary for launching the mass production of microchips, which is planned to be organized jointly with industrial partners during 2023, are currently being formed.
According to Viktor Anatolyevich, the results of the nanoheterostructure research project are the basis for the development of devices used in ultrafast and intelligent information systems capable of transmitting large amounts of information. Such equipment is currently being developed at LETI within the framework of the strategic project "New technologies of information connectivity of objects and territories".
"On the other hand, the production of such new components, the development and use of these communication systems rests on the need to process huge amounts of information. Classical artificial intelligence may not be able to cope with this task or solve it insufficiently effectively. For this purpose, as part of our third strategic project, we have developed the concept of a strong hybrid co-evolving, which will be able to develop in close conjunction with the user, based on his individual requests and characteristics. A new type of artificial intelligence will be in demand primarily in medicine and pharmaceuticals."
Vice-Rector for Scientific Work of SPBSET "LETI" Viktor Anatolyevich Tupik
In addition, now LETI is actively developing a direction that, in terms of its significance, can reach the level of a strategic project already this year, Viktor Anatolyevich added – we are talking about electrical engineering. In the course of its development, various types of power electric conversion devices are being developed, which are extremely in demand today in such branches of domestic industry as electromotion, energy and technosphere safety.
"Another major focus of our strategic program is focused on personnel policy. We understand that it is possible to solve the problem of training specialists for high-tech industries only by attracting young people to the research field. To do this, we are developing the scientific and educational infrastructure of the university and new training formats."
Vice-Rector for Scientific Work of SPBSET "LETI" Viktor Anatolyevich Tupik
Speaking about concrete steps, he noted that in 2022, eight new laboratories for electronics, materials science, device development and artificial intelligence research were created at LETI. Now they employ more than 100 young scientists. The university has also organized three acceleration programs, which have been successfully completed by more than 600 students from 10 universities in Russia."
**
"...three interrelated strategic projects: "Nanoheterostructural electronics, photonics and radiophotonics", which is the key, "New technologies of information connectivity of objects and territories", as well as "Technologies of strong hybrid intelligence for diagnosis, prevention, treatment and rehabilitation in applied medicine"."
~~

Наногетероструктурная электроника, фотоника и радиофотоника
Разработка интегральной компонентной базы на новых физических принципах с использованием новых материалов, и разработка базовых технологий ее промышленного производства
The goal of the strategic project is to develop an integrated component base based on new physical principles using new materials, and to develop basic technologies for its industrial production, which will form a new direction in the electronics industry: nanoheterostructural photonic integrated circuits.
Objectives of the strategic project
Development of a 9xx nm laser crystal for radiophotonic integrated circuits and pumping of high-power narrowband fiber lasers for space laser communication.
Development of pulsed radiation sources and ultra-high resolution digital matrix photodetector systems for space and lidar applications.
Development of technology for the synthesis of layered structures and nanostructures using new materials that provide the required refractive index contrast (dispersion), optical losses and other characteristics necessary to create FIS and components for them, including emitters, receivers, waveguide elements, as well as other active and passive optical components.
Topology development and prototyping of hybrid and integrated photonic circuits (such as random number generators, transceiver modules, spectrum analyzers, etc.).
Expected results of the strategic project
As a result of the project, new fundamental knowledge and practical results in the field of nanoheterostructural electronics, photonics and radiophotonics will be obtained. Basic technologies for the production of microwave electronics and photonics elements, including photonic integrated circuits, will be developed, prototypes of FIS for various functional purposes, such as monochromatic signal generators, frequency grid generators, noise and random number generators, spectrum analyzers and transceiver modules, will be created and put into production at the enterprises of industrial partners."

Новые технологии информационной связанности объектов и территорий
Цель проекта - к 2030 году войти в систему разделения труда ТОП-5 кластеров (R&D + production) на мировом рынке
The goal of the project is to enter the labor division system of the TOP 5 clusters (R&D + production) in the global NewRadio| 6G market by 2030, in terms of creating new principles and structural components of the NET–2030 ultra-broadband high-speed communication networks, including cognitive, hybrid, adaptive reconfigurable, heterogeneous, solving the problem of mastering new frequency bands, including subTHz.
It also provides for the transfer of high-tech solutions to key segments of the infocommunication market, for which a cumulative average annual growth rate is projected together with consortium members and industrial partners.
Objectives of the strategic project
Research and development of devices for generating, receiving and transmitting signals, promising antenna solutions and methods for controlling the electromagnetic field in mm and subTHz bands for NET-2030 systems and networks.
Construction of new radio access technologies (NewRadio|6G) of NET-2030 networks based on effective signal-code constructions and improved methods of multiple access.
Search for new principles of construction and development of cognitive reconfigurable systems of heterogeneous location and navigation.
Development of hardware and software complexes of the Internet of Everything (IoE) for the ecosystem of NET-2030 networks.
Ensuring the safety and security of data transmission in NET-2030 networks, the study of electromagnetic compatibility of nodes and structural elements of megasensory networks.
Expected results of the strategic project
Scientific and technical results:
Radio access technologies in promising NET-2030 networks using signal-code structures that are effective in a complex signal-interference environment.
Technologies for the design and manufacture of new antenna systems of mm- and sub-THz bands and the use of the principles of radiohologography in relation to the transition from classical diagram formation to the formation of optimal EMF distribution on objects.
Radiophotonic systems of transmission, reception and high-speed processing of signals and time series.
Innovative results:
Creation of a smart network of partners, including SME enterprises (small and medium-sized businesses) involved in the creation and sale of high-tech products in the field of wireless technologies.
Providing the IoE infocommunication environment by building intelligent multi-band systems as a result of the integration and development of wireless technologies.
Creation of test zones of new generation networks that ensure the implementation of ultra-high-speed digital services.
Creation of a line of promising R&D products of the "Smart Radio Environment" direction – SmartField, SmartRadioArch, SmartSpectrum (including together with foreign partners – Aalto University, Keysight Technologies, Rohde &Schwarz).
Results in the field of personnel training:
Development and implementation of educational programs at all levels for advanced training in the field of radio electronics and infocommunication technologies.
Organization of youth collectives for project educational and research work by introducing R&D projects as a basic element of Master's degree educational programs.
Development and implementation of additional professional education programs in order to transform the current personnel of the industry to a new technological way, including with the involvement of resources of international manufacturers of measuring equipment Keysight Technologies, Rohde &Schwarz.

Технологии сильного гибридного интеллекта для прикладной медицины
Технологии сильного гибридного интеллекта для диагностики, профилактики, лечения и реабилитации в прикладной медицине

The aim of the project is to develop the fundamentals of Strong Hybrid Intelligence (SHI) with the construction of a technological stack based on it for the intellectualization of economic sectors and its testing in the field of applied medicine.
Objectives of the strategic project
Fundamental research. Development of a mathematically based concept of strong hybrid intelligence; approaches to ensuring the interoperability (compatibility) of human and machine intelligence in solving complex problems; principles of modeling and description of cognitive functions.
Applied solutions. Development of a technological platform for building solutions based on SHI; development of frameworks for rapid prototyping, creation and implementation of products based on SHI.
Approbation and implementation. Development and implementation of a complex of software and hardware for solving problems of practical medicine.
Education. Creation of a multi-level system of training specialists for research, development and application of solutions based on SHI.
Organizational measures and development of the region. Organization of activities for the search for new concepts for the construction of SHI, prototyping products based on it and their testing at all stages of the life cycle based on the Living Lab model; creation of experimental legal regimes supporting the processes of development, testing and implementation of a full cycle of obtaining new knowledge, creating innovative breakthrough technologies, products and services based on SHI and promoting socio-economic development of regions through technology transfer in the field of applied medicine.
Expected results of the strategic project
As a result of the project, new fundamental knowledge and practical results in the field of nanoheterostructural electronics, photonics and radiophotonics will be obtained. Basic technologies for the production of microwave electronics and photonics elements, including photonic integrated circuits, will be developed, prototypes of FIS for various functional purposes, such as monochromatic signal generators, frequency grid generators, noise and random number generators, spectrum analyzers and transceiver modules, will be created and put into production at the enterprises of industrial partners.
1.Results of fundamental research
1.1.Mathematically based concept of building a strong hybrid intelligence.
1.2.The concept of interoperability (compatibility) of interacting intelligent agents based on human and machine intelligence at different levels (neural interfaces, cognitive and semantic communication).
1.3.The concept of dynamic formation of knowledge ontologies in a hybrid environment.
1.4.The concept of coevolution of the hybrid intelligence system.
1.5.Description of the principles of ensuring the safety and ethics of the use of SHI.
2.Results of development of applied solutions
2.1.Software and hardware platform for building intelligent systems based on the SHI (GI operating core).
2.2.A software framework for rapid prototyping, creation and implementation of products based on SHI.
3.Results of approbation in the field of applied medicine
3.1.A complex of software and hardware systems, including:
3.1.1.Software and hardware system to support research and development of human cognitive functions for the construction of GI, assessment of the level of its evolution and correction of the trajectory of its formation.
3.1.2.A system based on the SHI to support research, training, situational behavior analysis and certification of medical workers using a digital double of the human body.
3.1.3.A system for supporting research and training of the SHI system when assisting a doctor in outpatient and inpatient treatment with predicting outcomes, determining risks and preventing diseases based on monitoring the patient's condition.
3.1.4.Neurorehabilitation system based on neuroplasticity management, virtual reality, system model of motor control.
3.1.5.A system of predictive analytics on the health status of individuals and cohorts of the population in certain conditions caused by natural and social factors.
3.1.6.A system of remote monitoring of human health based on the model of the digital twin of the human body and the concept of federated learning.
3.1.7.A system for improving the effectiveness of the training process.
3.2.A technology stack for working with an individual digital medical history of a person based on a private cloud.
3.3.A biointerface harmonized with a person, including the possibility of compensating for the lost functions of the body and its non-pharmacological correction.
3.4.Nanocarriers of drugs for their targeted delivery to organs with a histohematic barrier.
3.5.Mobile biomedical expert diagnostic systems based on multimedia data analysis.
3.6.Express diagnostic systems based on multimodal biochips.
4.Educational outcomes
4.1.A system of continuous training in technologies for diagnosis, prevention, treatment and rehabilitation within the framework of the concept of SHI in applied medicine.
4.2.Network and modular educational programs of basic and additional education on:
- fundamental and applied aspects of the development of SHI;
- development of solutions based on the SHI, including for the tasks of applied medicine.
5.Results of organizational measures and impact on the development of the region
5.1.Distributed research ecosystem based on the Living Lab model.
5.2.Regulatory "sandbox" for working out the legal aspects of the use of SHI in medical tasks.
5.3.School of key researchers in the field of artificial intelligence.
~~
STRATEGIC PROJECTS

Новые электронные компоненты и устройства для сверхбыстрых и интеллектуальных информационных систем
Разработка интегральной компонентной базы на новых физических принципах с использованием новых материалов, и разработка базовых технологий ее промышленного производства

The goal of the strategic project is to develop a new ECB to overcome the technological barrier caused by the achievement of the maximum technological and functional parameters of traditional silicon electronics, in order to create industrially oriented ultrafast intelligent trusted systems. It is achieved through the development and use of new photonic principles of information processing, neuromorphic and neural network models of computing and new generation devices.
Objectives of the strategic project
Development of a new component base technology based on photonic integrated circuits (FIC).
Development of the basic technology of power electronics based on silicon carbide (SiC).
Development of "smart" photonic sensors and networks based on them for the construction of human-machine systems using hybrid intelligence technologies, including unmanned aircraft systems.
Design of microwave monolithic integrated circuits for applications critical in basic parameters in unmanned systems, including those with group control.
Development of ground-based monitoring, management and security points based on the concept of a wireless information environment.
Design of safe unmanned systems based on methods and technologies of neuromorphic networks and hybrid artificial intelligence.
Development and manufacture of energy-efficient electric propulsion systems using the SiC component base.
Expected results of the strategic project
A series of FIC of various functional purposes for use in quantum computing and quantum communications systems, control systems and organization of interaction of unmanned vehicles.
The technology of defect-free single crystals and SiC epitaxial layers for the production of medium-power Schottky diodes used in energy-efficient electric propulsion systems.
Manufacturing technology and design of smart sensors for various purposes for biomedical and unmanned systems.
Experimental samples of fiber-optic and integrated photonic semiconductor sensors.
Elements and devices of heterostructural solar energy to ensure the energy efficiency of unmanned objects.
A prototype of a ground-based system for detecting and tracking unmanned objects.
Software and hardware solutions to ensure the autonomy of unmanned systems, including the management of groups of UAVs.
Designs of power inverters and rectifiers based on SiC component base."